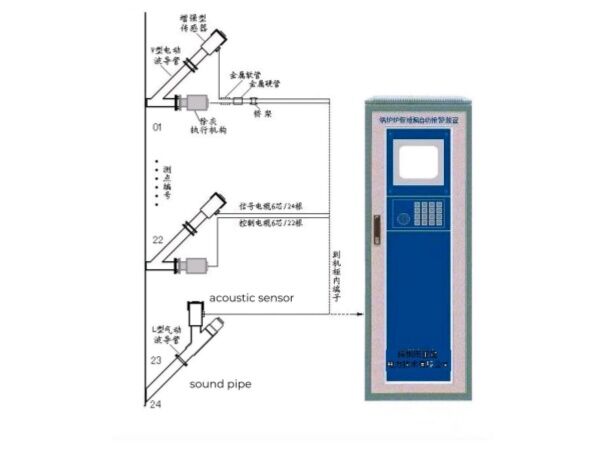
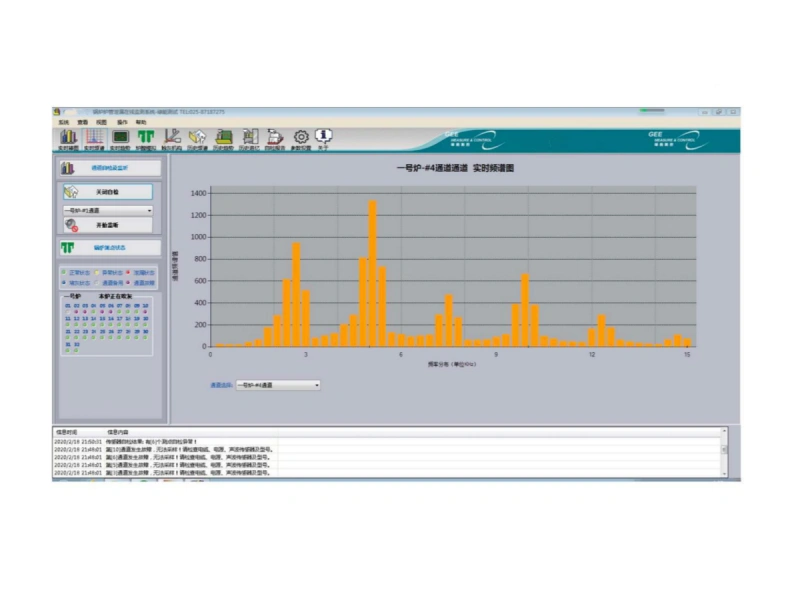
Boiler tube leak detection
Advanced Boiler Tube Leak Detection System – Protect Your Operations with Precision
Ensure the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your boiler systems with our cutting-edge boiler tube leak detection. Designed for industries relying on steam generation, our solution provides real-time monitoring, early leak detection, and pinpoint accuracy to prevent costly downtime, equipment damage and safety hazards.
Our system uses air borne or metal borne acoustic sensor with high sensitivity to collect boiler noises, and execute spectrum analysis by Fast Fourier Transform to find and identify tiny leaks at early stage.
Why Choose Our Boiler Tube Leak Detection System?
- Real-Time Monitoring & Alerts
Our system continuously monitors boiler tubes, instantly detecting even the smallest leaks. With real-time alerts, you can take immediate action to minimize operational disruptions and avoid costly repairs.
- High Accuracy & Precision
Utilizing advanced acoustic emission (AE) technology, our system accurately locates leaks, even in the most complex boiler configurations. This ensures quick identification and resolution of issues.
- Compatible with All Boiler Types
Whether you operate recovery boilers, utility boilers, or industrial steam boilers, our solution is designed to integrate seamlessly with your existing infrastructure.
- User-Friendly Interface
Our intuitive control interface makes it easy for operators to monitor boiler health, view diagnostics and manage alerts—all from a single platform.
- Proven Reliability
Trusted by leading industries worldwide, our system has a track record of reducing maintenance costs, extending boiler lifespan, and enhancing operational safety.
Sensitive Sensor
Sensitivity: >25mV/Pa
Output voltage: 0~900mV(AC)
Frequency range: 0~20kHz
Measurement range: Hemisphere space with diameter ≤12m
Working temperature: -40~+105℃
Application
Whether CFB boiler, pulverized coal fired boiler or heat recovery steam generator (HRSG), tube leak detection system could bring tubes of furnace waterwall, superheater, reheater, economizer under monitoring. Our leading technology enables plants to find and locate early tube leaks, then take actions before they escalate into major failures.
Function
- In-time detection and early alert to maximize production and revenue of power plant.
- Tell the location of tube leaks without sending people to hard-to-access areas
- Follow up on leakage condition and trend.
- Show frequency spectrum of sound wave and display in bar chart on computer screen.
- Find out abnormal working status of soot blower.
- Interface with DCS and telecommunication to achieve remote monitoring, diagnosis and maintenance.
- Acoustic data can be stored for 12 months. Data printing and query is available.
Benefits
- Tiny leaks, which can’t be heard by patrol people at site, can be detected to avoid massive loss. It brings asset and personnel safety to a higher level.
- 24/7 monitoring on leakage condition puts operator on informed position to make optimal decision.
- Quick location identification allows less time spent on looking for leaks and more time on planned shutdown.
- Early detection can reduce plant downtime and repair expense.
- Minimize secondary damage to neighboring tubes.
Online monitoring and detection for boiler tube leaks is worthy for modern power plants. Financial savings created by acoustic detection system will be much higher than investment on equipment even at the first event.